Atomic Force Microscopy:
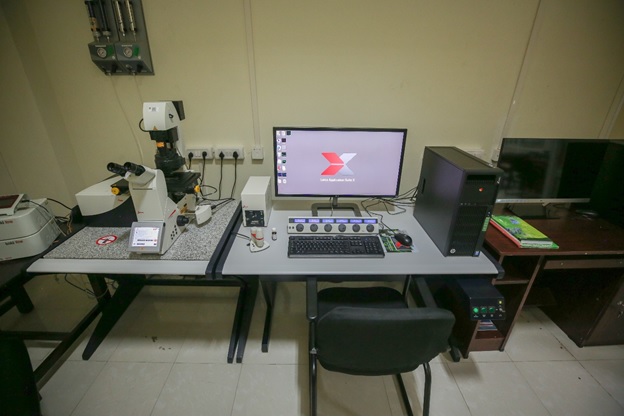
AFM: The AFM consists of a cantilever with a sharp tip at its end that is used to scan the specimen surface. The cantilever is typically silicon nitride with a tip radius of curvature on the order of nanometers. When the tip is brought into proximity of a sample surface, forces between the tip and the sample lead to a deflection of the cantilever according to Hooke’s law. The forces are measured in AFM include mechanical contact force, van der waals forces, capillary forces, chemical bonding, electrostatic forces, magnetic forces etc.
Measurement provides topographic (height) information or size (height/thickness) distribution in solid samples (soft/hard materials) under ambient conditions.
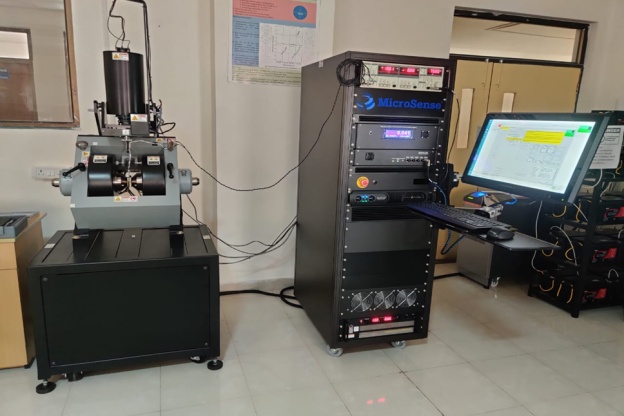
General Information: Make – Nanosurf (Switzerland), Model – CoreAFM, Year of Installation – 2024.
Features: Maximum scan range XYZ up to 100 x 100 x 12 μm, Cameras for tip surface distance adjustment, Data acquisition and analysis software
Imaging Modes: Static force, Dynamic force, Phase Contrast, Lateral force, Standard spectroscopy, Force Modulation, Standard lithography, Standard Conductive AFM, EFM, MFM, Liquid cell imaging
Sample Requirements:
1. Specimen Size- Samples up to 100* 100 mm in size and 10mm in thickness.
2. Sample Requirement- Film-type samples.
Location: Analytical Lab- I, D228, Chemical Engineering



 An Institute of Eminence
An Institute of Eminence