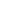
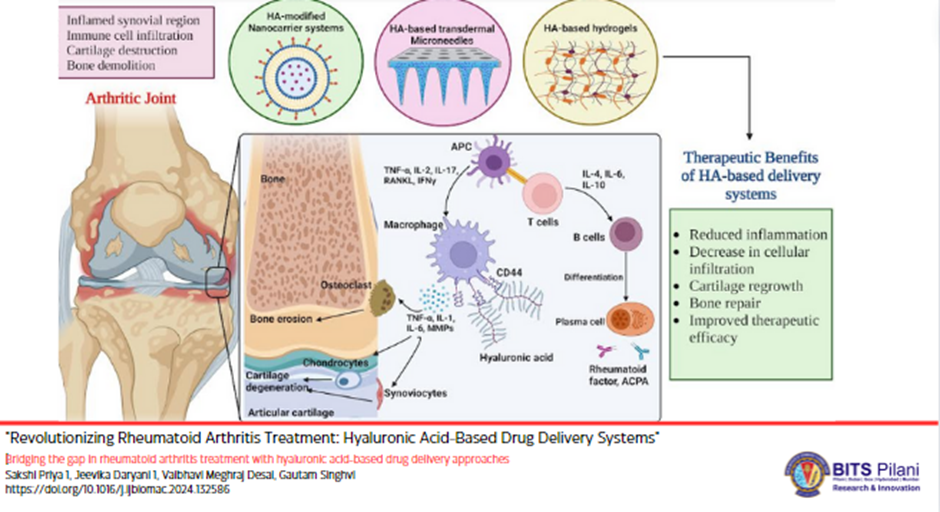
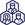
In the realm of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treatment, innovative approaches are continually emerging to improve therapeutic outcomes and patient’s quality of life. Among these advancements, the use of hyaluronic acid (HA) in drug delivery systems has garnered significant attention. Researchers like Sakshi Priya, Jeevika Daryani, Vaibhavi Meghraj Desai, Gautam Singhvi have been at the forefront of exploring how HA-based technologies can revolutionize RA treatment. HA-based nanocarriers, hydrogels, and microneedles offer targeted and efficient drug delivery, reducing side effects and improving patient adherence. HA-coated nanoparticles and microparticles have been developed to deliver drugs to inflamed joints in a targeted manner, showing improved drug encapsulation, sustained release, and enhanced cellular uptake compared to uncoated systems. HA-based microneedle patches provide a safe and effective alternative to subcutaneous injections for transdermal drug delivery. These HA-based drug delivery systems show promise for the treatment of RA by improving drug delivery, targetability, and therapeutic efficacy.
Key Insights
- HA-based drug delivery systems offer targeted and efficient drug delivery for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
- HA-coated nanoparticles and microparticles show improved drug encapsulation, sustained release, and enhanced cellular uptake compared to uncoated systems.
- HA-based microneedle patches provide a safe and effective alternative to subcutaneous injections for transdermal drug delivery.
- HA-based formulations have the potential to improve drug delivery, targetability, and therapeutic efficacy in the treatment of RA.
- Further research and optimization are needed to overcome challenges and fully harness the benefits of HA-based drug delivery systems for RA management.
Rheumatoid arthritis, often known as RA, is a chronic inflammatory and auto-immune illness that is primarily linked to the deterioration of the synovial linings that are found in the joints. The people who are affected by this disease have a shorter life span because it is a progressive condition. For the purpose of developing more effective and target-specific drug delivery alternatives for RA, nanoparticles that contain hyaluronic acid (HA) have recently come to the forefront. Synovial fluid contains a significant amount of HA, which functions as a natural ligand for the CD44 receptors due to its presence. The targeted delivery strategy that uses CD44 as the target has the potential to assist in reducing the amount of medicine that is distributed off-target. These HA-based surface-decorated nanocarriers, hydrogels, and MNs are cutting-edge techniques that offer customized delivery, less side effects, and more patient adherence in order to solve the prevalent difficulties that are associated with RA therapy. Due to the aforementioned facts, the purpose of this review is to address the role of HA in the development of more efficient formulations for therapeutic delivery in the treatment of RA. Additionally, it offers a detailed analysis of the prospective developments, primarily in the treatment of RA through the use of HA-based drug delivery systems, including topical, transdermal, and parenteral administration, along with pertinent case reports.
The benefits of HA-based non-conventional formulations for the management of RA are also explored, such as HA-based surface-decorated nanocarrier systems ensuring specific targeting of drugs to inflamed joints, enhancing therapeutic efficacy and reducing off-target distribution of drugs; HA-based hydrogels drug delivery systems ensure sustained and controlled drug release, maintaining consistent therapeutic levels and reducing the frequency of administration; and HA-based advanced microneedle drug delivery system offer a minimally invasive approach for the delivery of the drug, improving patient compliance and adherence while enabling targeted administration to affected sites.
Even though HA-modified nanoparticles have shown to be quite effective in treating RA, there are still certain difficulties related with the use of HA. Despite the fact that it is completely risk-free, there are certain infections and hypersensitivity problems that are linked to the use of therapies that involve its application. A long-term safety profile for the utilization of HA-based therapeutic techniques in the field of rheumatology is something that needs to be established. Because HA has a short half-life and limited bioavailability, the formulations need to be modified to compensate for these characteristics. The challenges that currently exist and the possible avenues that remain for future research are also discussed. These limitations can be overcome if proper preparation and optimization techniques are applied. From a general standpoint, HA-based nanocarriers can be manufactured by implementing particular modifications to deliver medications to target sites in an effective manner. This is a huge step forward in the field of rheumatology and the treatment of the condition since it has the potential to successfully manage the progression of diseases for patients.


 An Institute of Eminence
An Institute of Eminence